WebDriver is a remote control interface that enables introspection and control of user agents. As such it can help developers to verify that their websites are working and performing well with all major browsers. The protocol is standardized by the W3C and consists of two separate specifications: WebDriver classic (HTTP) and the new WebDriver BiDi (Bi-Directional).
This newsletter gives an overview of the work we’ve done as part of the Firefox 127 release cycle.
Contributions
Firefox – including our WebDriver implementation – is developed as an open source project, and everyone is welcome to contribute. We are always grateful to receive external contributions, here are the ones which made it in 127:
- Victoria simplified our implementation of the “Is Element Enabled” command for WebDriver classic in order to use regular DOM APIs instead of an external helper imported from Selenium. This cleanup will also make this command easier to maintain in the future.
- Gravyant added a new
isInstanceassertion helper which can be used in the WebDriver codebase to check that a given object is an instance of a specific class.
WebDriver code is written in JavaScript, Python, and Rust so any web developer can contribute! Read how to setup the work environment and check the list of mentored issues for Marionette.
General
Bug fixes
- Fixed a bug with the
"wheel"action, which can be used both in WebDriver BiDi and WebDriver classic. We now correctly handle modifier keys such asShift,Control, etc. With this, you can simulate a user action scrolling the wheel while holding a modifier.
WebDriver BiDi
New: Support for the “permissions.setPermission” command
The permissions module is an extension to the WebDriver BiDi specification, defined in the Permissions specification. It is the first extension for WebDriver BiDi to be implemented in Firefox, with the permissions.setPermission command. This command allows you to grant, deny or prompt for a given permission, such as “geolocation”. The permission will be set for a provided origin, and optionally for a specific user context.
The descriptor argument should be a Permission Descriptor, which is basically an object with a name string property set to the name of the permission to update. The state argument should be one of "granted", "denied" or "prompt". The origin argument should be the origin for which the permission setting will be set. And finally the optional argument userContext should be the user context id where the permission should be applied ("default" if omitted).
Below is an example of setting the "geolocation" permission to "prompt" for the "https://www.google.com" origin:
-> {
"method": "permissions.setPermission",
"params": {
"descriptor": {
"name": "geolocation",
},
"state": "prompt",
"origin": "https://www.google.com"
},
"id": 2
}
<- { "type": "success", "id": 2, "result": {} }Afterwards, trying to use a geolocation feature on a website with the “https://www.google.com” origin such as Google Maps will trigger the permission prompt as shown below:
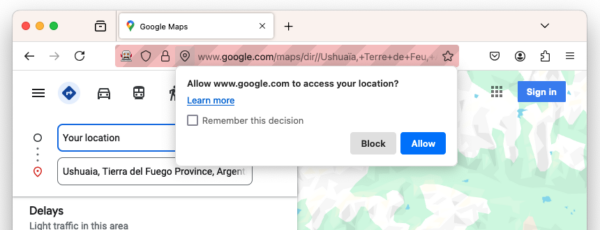
"geolocation" permission promptNew: Support for accessibility locator in the “browsingContext.locateNodes” command
The accessibility locator allows you to find elements matching a specific computed role or accessible name. This locator has the type "accessibility", and for the value it expects an object with a "name" property (for accessible name) and/or a "role" property (for computed role). You may provide one or both properties at the same time. Note that the start nodes (startNodes argument) can contain elements, documents and document fragments.
For instance, considering the following markup, which attributes the checkbox role to a span, labelled by another span element:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<span role="checkbox" aria-checked="false" tabindex="0" aria-labelledby="tac"
></span>
<span id="tac">Checkbox name</span>
</body>
</html>You can find the checkbox element either by using the “role” accessibility locator:
{
"method": "browsingContext.locateNodes",
"params": {
"locator": {
"type": "accessibility",
"value": {
"role": "checkbox"
}
},
"context": "2a22b1c6-6fa8-4e62-b4af-32ed2ff1ced7"
},
"id": 19
}Or by using the accessible name, which is the value of the aria-labelledby element:
{
"method": "browsingContext.locateNodes",
"params": {
"locator": {
"type": "accessibility",
"value": {
"name": "Checkbox name"
}
},
"context": "2a22b1c6-6fa8-4e62-b4af-32ed2ff1ced7"
},
"id": 20
}Both commands will return the span with role="checkbox":
{
"type": "success",
"id": 20,
"result": {
"nodes": [
{
"type": "node",
"sharedId": "16d8d8ab-7404-4d4b-83e9-203fd9801f0a",
"value": {
"nodeType": 1,
"localName": "span",
"namespaceURI": "http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml",
"childNodeCount": 0,
"attributes": {
"role": "checkbox",
"aria-checked": "false",
"tabindex": "0",
"aria-labelledby": "tac"
},
"shadowRoot": null
}
}
]
}
}New: Support for “devicePixelRatio” parameter in the “browsingContext.setViewport” command
We now support the devicePixelRatio parameter in the browsingContext.setViewport command, which allows to emulate the behavior of screens with different device pixel ratio (such as high density displays). The devicePixelRatio is expected to be a positive number.
Bug fixes
- We fixed a race condition in
browsingContext.navigatewhich could lead to unnecessary waiting when creating new tabs.
Marionette (WebDriver classic)
Bug fixes
WebDriver:ElementClearnow works as expected with elements nested in a disabledfieldset.- We fixed a bug with
WebDriver:GetElementTextwhich failed to correctly capitalize text containing an underscore (_). WebDriver:SwitchToFramewill no longer fail when called in the middle of an ongoing navigation.
Leave a Reply