WebDriver is a remote control interface that enables introspection and control of user agents. As such it can help developers to verify that their websites are working and performing well with all major browsers. The protocol is standardized by the W3C and consists of two separate specifications: WebDriver classic (HTTP) and the new WebDriver BiDi (Bi-Directional).
This newsletter gives an overview of the work we’ve done as part of the Firefox 129 release cycle.
Contributions
Firefox – including our WebDriver implementation – is developed as an open source project, and everyone is welcome to contribute. There were no external contributions during the Firefox 129 release cycle, but we already have 3 bugs fixed by external contributors for the next release! If you ever wanted to contribute to an open source project used by millions of users, or are interested in some experience in software development, jump in. We have many beginner-friendly available over at https://codetribute.mozilla.org/ and the documentation to get started is easy to follow.
General
Disabling CDP (Chrome DevTools Protocol) by default
As announced in our previous blog post (Deprecating CDP support in Firefox), with Firefox 129 CDP is now disabled by default. Our WebDriver BiDi implementation now provides more features than the experimental CDP support, so we strongly encourage all users relying on CDP to try out WebDriver BiDi. Please reach out to us if you stumble on any issue while trying to migrate to WebDriver BiDi. For the time being, you can still re-enable CDP by setting the remote.active-protocols preference to 2 (CDP only) or 3 (CDP+BiDi).
WebDriver BiDi
Added the network.setCacheBehavior command
The network.setCacheBehavior command allows to change the network cache behavior either globally or for a set of top-level browsing contexts. Disabling the network cache during tests can be useful if you want to ensure consistent results between test runs, without having to worry about the heuristics used by the browser in order to use the cache or not. It’s also recommended to disable the cache when using network interception features. This command expects a cacheBehavior parameter which can either be "default" or "bypass". Using "bypass" will instruct the browser to bypass the cache, in other words it will disable the network cache. You can also provide an optional contexts parameter, which should be an array of top level context ids.
-> {
"method": "network.setCacheBehavior",
"params": {
"cacheBehavior": "bypass",
"contexts": [ "08706bf7-1b79-4f92-bbd1-d066c469ed8f" ]
},
"id": 61
}
<- { "type": "success", "id": 61, "result": {} }Note that you can call the command several times to apply different cache behaviors to different top-level contexts. You can for instance set the cache behavior to "bypass" globally first, and then selectively reset it do "default" for one or more contexts. However note that calling network.setCacheBehavior globally (ie. with no contexts argument) will override any specific behavior previously set for a context.
Support for “beforeUnload” type prompts
We now support the user prompts of type "beforeUnload", which can be triggered from the "beforeunload" event on a webpage. The usual user prompt events will be emitted for those prompts: browsingContext.userPromptOpened, browsingContext.userPromptClosed. And you can handle the prompts using the existing browsingContext.handleUserPrompt command.
In the example below, the client listens for user prompt events, and will dismiss the "beforeUnload" user prompt detected:
<- {
"type": "event",
"method": "browsingContext.userPromptOpened",
"params": {
"context": "08706bf7-1b79-4f92-bbd1-d066c469ed8f",
"handler": "ignore",
"message": "This page is asking you to confirm that you want to leave — information you’ve entered may not be saved.",
"type": "beforeunload"
}
}
-> {
"method": "browsingContext.handleUserPrompt",
"params": {
"context": "08706bf7-1b79-4f92-bbd1-d066c469ed8f",
"action": "dismiss"
},
"id": 63
}
<- {
"type": "event",
"method": "browsingContext.userPromptClosed",
"params": {
"context": "08706bf7-1b79-4f92-bbd1-d066c469ed8f",
"accepted": true,
"type": "beforeunload"
}
}
<- {
"type": "success",
"id": 63,
"result": {}
}Support optional arguments for network.provideResponse
For requests intercepted in the beforeRequestSent phase, we now support all the optional arguments for the network.provideResponse command. The newly supported arguments are body, cookies, headers, reasonPhrase and statusCode. With this, you can now easily return mocked responses for any intercepted request. This request will not actually reach the network and instead the information you provided will be used to build a functional response. The names are quite self-explanatory: body allows to set the response body, cookies is a shortcut to add Set-Cookie headers, headers sets the regular response headers, reasonPhrase is the response’s status text (for instance "OK") and statusCode is the response’s status code (for instance 200).
In the following example, the client intercepts requests to a "script.js" URL and will use network.provideResponse to return a custom script which will log a message. We will then navigate to a page which tries to load this "script.js" file and we expect to receive a log.entryAdded event corresponding to the mock response.
First we setup the intercept and navigate to the test page.
-> {
"method": "network.addIntercept",
"params": {
"phases": [
"beforeRequestSent"
],
"urlPatterns": [
{
"type": "string",
"pattern": "https://test-provideresponse-mock-script.glitch.me/script.js"
}
]
},
"id": 67
}
<- { "type": "success", "id": 67, "result": { "intercept": "876a5b3d-045b-49ca-80e4-c61de1d0d00d" } }
-> {
"method": "browsingContext.navigate",
"params": {
"context": "0f38a9a6-912c-4e83-9945-9aa8b9ee1f1f",
"url": "https://test-provideresponse-mock-script.glitch.me",
"wait": "none"
},
"id": 70
}
<- {
"type": "success",
"id": 70,
"result": {
"navigation": "89535996-58ea-4b18-b95e-43af6c137ecf",
"url": "https://test-provideresponse-mock-script.glitch.me/"
}
}Several network events will be received, but here we are only interested in the blocked one, which will be resumed using network.provideResponse:
<- {
"type": "event",
"method": "network.beforeRequestSent",
"params": {
"context": "0f38a9a6-912c-4e83-9945-9aa8b9ee1f1f",
"isBlocked": true,
"request": {
"request": "41",
"url": "https://test-provideresponse-mock-script.glitch.me/script.js",
[...]
},
"intercepts": ["876a5b3d-045b-49ca-80e4-c61de1d0d00d"],
[...]
}
}
-> {
"method": "network.provideResponse",
"params": {
"request": "41",
"body": {
"type": "string",
"value": "console.log('Log from provideResponse script')"
},
"headers": [
{
"name": "Content-Type",
"value": {
"type": "string",
"value": "text/javascript"
}
}
],
"reasonPhrase": "OK",
"statusCode": 200
},
"id": 73
}
<- { "type": "success", "id": 73, "result": {} }Finally we receive the expected log.entryAdded event, which shows that the script was correctly received and handled by the test page.
<- {
"type": "event",
"method": "log.entryAdded",
"params": {
"type": "console",
"method": "log",
"source": {
"realm": "765fbec6-14e0-427c-9984-527010763fcd",
"context": "0f38a9a6-912c-4e83-9945-9aa8b9ee1f1f"
},
"args": [
{
"type": "string",
"value": "Log from provideResponse script"
}
],
"level": "info",
"text": "Log from provideResponse script",
"timestamp": 1722860802687
}
}New handler field for browsingContext.userPromptOpened
The browsingContext.userPromptOpened event now contains an additional "handler" field which contains the user prompt handler type ("accept", "dismiss" or "ignore") configured for the prompt which triggered the event. The user prompt handler type can be configured via the unhandledPromptBehavior capability.
New originalOpener field for the BrowsingContextInfo type
The BrowsingContextInfo type now includes an "originalOpener" field which contains the context id of the context from which the browsing context was opened. For instance if the browsing context was created using window.open or by clicking on a link from another page, the "originalOpener" field will contain the context id of this page (even if the link has rel=noopener). If the context was not created from another page (for instance using the browser UI, or using the browsingContext.create command), the "originalOpener" field will have the value null.
See the example below, with a first window created manually, and a second one created using a rel=noopener link.
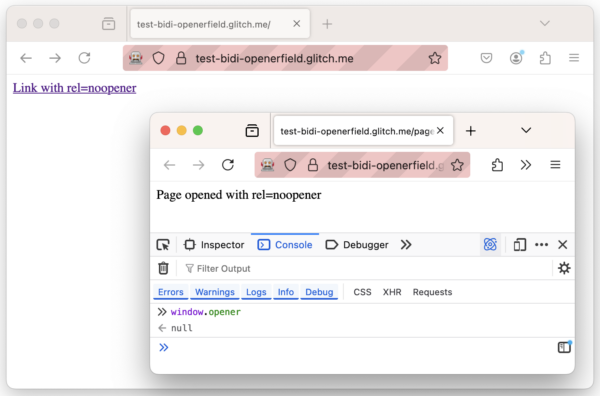
rel=noopener link, window.opener is null in the ConsoleAs you can see in the browsingContext.getTree result below, the first window has "originalOpener" set to null, because it was created using the Firefox UI. And the second window has the same field set to the context id of the first window (even though window.opener is null because we used a rel=noopener link).
{
"type": "success",
"id": 6,
"result": {
"contexts": [
{
"children": [],
"context": "dab18807-4b2e-4b10-b046-5c60c2b15811",
"originalOpener": null,
"url": "https://test-bidi-openerfield.glitch.me/",
"userContext": "default",
"parent": null
},
{
"children": [],
"context": "6142ff68-1185-4a9f-b08e-0932d797ef15",
"originalOpener": "dab18807-4b2e-4b10-b046-5c60c2b15811",
"url": "https://test-bidi-openerfield.glitch.me/page2.html",
"userContext": "default",
"parent": null
}
]
}
}Added support for data URLs with network events
Starting with Firefox 129, you will receive network events (network.beforeRequestSent, network.responseStarted and network.responseCompleted) for requests using data URLs. Note that those requests cannot be intercepted. At the moment we only emit events for navigation requests, but this limitation should be lifted in Firefox 130.
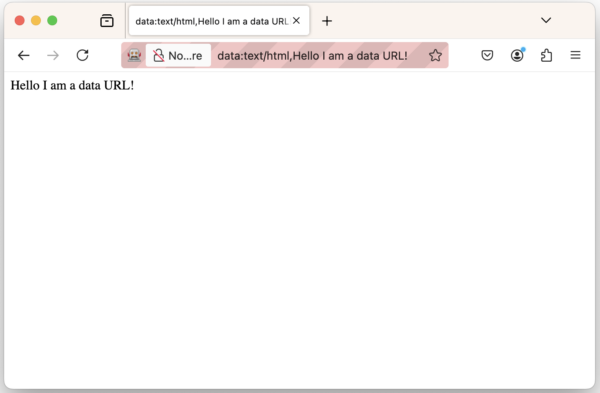
A snippet from the network.responseCompleted event corresponding to the page displayed above can be found below:
{
"type": "event",
"method": "network.responseCompleted",
"params": {
"context": "307aaff5-164a-4e88-9453-cdddd26ad748",
"isBlocked": false,
"navigation": "25df080a-5492-4f53-b68c-b2dc685c202f",
"redirectCount": 0,
"request": {
"request": "7",
"url": "data:text/html,Hello I am a data URL!",
"method": "GET",
[...]
},
"timestamp": 1722873995763,
"response": {
"url": "data:text/html,Hello I am a data URL!",
"protocol": "data",
"status": 200,
"statusText": "OK",
"fromCache": false,
[...]
}
}
}Support for the promptUnload argument for browsingContext.close
The new argument promptUnload for browsingContext.close allows to bypass "beforeUnload" type prompts. This argument is a boolean, set it to true in order to show "beforeUnload" prompts or to false to bypass them. This parameter is optional, and if omitted it will default to false (meaning "beforeUnload" prompts will be bypassed).
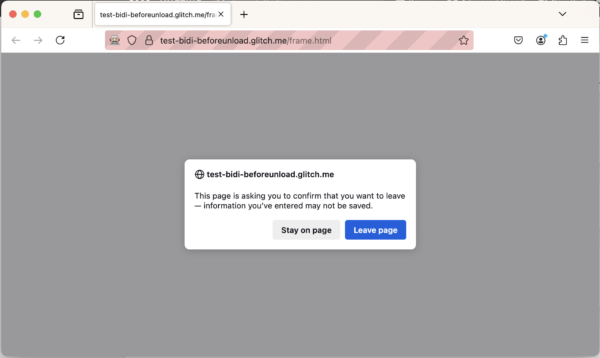
promptUnload=true to allow "beforeUnload" prompts with browsingContext.close Bug fixes
- Fixed a bug in
network.continueRequestwhere you could not set multiple values for the same header. - Fixed a bug for the
unhandledPromptBehaviorcapability, which could not be used with BiDi only sessions. - Fixed a bug with
session.endandbrowser.closewhich would unexpectedly fail when no Marionette client was connected. - Fixed a bug with
browsingContext.navigatewhich would fail to resolve if a same-document navigation started on “beforeunload”. - Improved the
browser.closecommand to discard all “beforeunload” prompts when closing the top-level browsing contexts. - Fixed a bug in the
browsingContext.userPromptOpenedevent, which would unexpectedly miss thedefaultValuefield. - Fixed an issue with the
network.responseCompletedevent during authentication flows, which was emitted too many times compared to the specifications. Only oneresponseCompleted(orfetchError) event is expected for the whole HTTP authentication flow. - Improved the
browser.removeUserContextcommand to skip all “beforeunload” prompts.
Leave a Reply